In this article, from the series of articles of GeeTech Group, we will learn about the Residual Current Devices and talk about its uses, structure and types.
Table of contents of this article
- how do residual current devices work
- types of residual current device
- What is RCD test
- siemens residual current device
- abb residual current devices
- residual current device schneider
- residual current device price
what is a residual current device
An RCD, or residual current device, is a life-saving device designed to prevent fatal electric shocks. It keeps you safe by cutting off the power if you touch something live, like a bare wire. It can even offer protection against electrical fires! Unlike ordinary fuses and circuit-breakers, RCDs provide an extra level of personal safety.
Residual current devices (RCDs) serve as crucial safety devices that provide automatic electricity shut-off in the event of a fault. Compared to standard fuses and circuit-breakers, RCDs exhibit higher sensitivity, offering enhanced protection against electric shock.
The presence of moisture elevates the risk of electric shock, making RCDs particularly crucial in settings prone to wet conditions, including bathrooms and gardens. These devices effectively safeguard against possible electric shocks in areas where individuals may come into contact with water.
When operating electrical equipment outdoors, it is imperative to utilize RCD protection. Without such protection, seemingly ordinary tasks like mowing the lawn can turn perilous if the electrical lead is accidentally severed. An RCD can avert potential dangers and ensure the safety of individuals working around electrical equipment outdoors.
how do residual current devices work
An RCD constantly monitors the electrical current in protected circuits. If it detects any unintended current flow, such as through a person touching a live part, it swiftly switches off the circuit, greatly reducing the risk of serious harm or even death.
Inside an RCD, there’s an iron core. The live current passes through a switchgear and a coil wrapped around the iron core. As the current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field.
Conversely, the current returning through the neutral wire passes through a coil wired in the opposite direction. This creates two opposing magnetic fields. Under normal circumstances, these fields balance each other out, keeping everything running smoothly.
However, if a fault occurs in an appliance and some electricity leaks to the ground, there will be an imbalance between the magnetic fields. The net magnetic field triggers the switchgear, which includes an iron panel attracted to the iron core. This action breaks the circuit, protecting you from potential harm.
RCDs come with a reset button to restore normal operation after a fault has been resolved. Stay safe and secure with reliable RCD technology!
types of residual current device
Let’s explore the different types of RCDs to ensure comprehensive protection for various electrical scenarios. According to IEC 60755 standards, multiple RCD types are available to handle different forms of residual current and load characteristics.
Type AC RCDs:
These RCDs detect alternating currents and are suitable for general use, covering a wide range of applications.
Type A RCDs:
Offering both residual current and alternating current detection, Type A RCDs are specifically designed for single-phase class 1 electronic loads.
Type F RCDs:
Building upon the detection characteristics of Type A RCDs, Type F RCDs excel in circuit protection where single-phase variable-speed drivers are utilized.
Type B RCDs:
Ideal for loads with three-phase rectifiers such as variable speed drives, PV systems, EV charging stations, and medical equipment.
Additionally, RCDs can be categorized as follows:
Fixed RCDs:
These RCDs are installed within a consumer unit or fusebox, safeguarding not only individuals interacting with the unit but also the circuits connected to it. Fixed RCDs provide extensive protection, ensuring safety for both wiring and sockets on a circuit.
Socket-Outlet RCDs:
Specially designed socket-outlets incorporating built-in RCDs serve as replacements for standard sockets, providing added protection for individuals in contact with connected equipment.
Portable RCDs:
Designed to be plugged into standard socket-outlets, portable RCDs offer convenience and versatility. Appliances can be connected to the portable RCD, which acts as an intermediary for heightened protection.
Stay secure and choose the appropriate type of RCD for your specific electrical needs!
What is RCD test
It’s crucial to ensure that RCDs are correctly installed in your property or circuit board and regularly tested. The good news is that RCDs are easily testable and resettable devices, equipped with test and reset buttons for convenience.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on testing an RCD:
1. Plug a small lamp appliance into a socket and ensure that it is functioning properly. Keep the lamp turned on.
2. Confirm that the electricity is securely connected to the RCD, and the main switch is in the ‘on’ position.
3. Turn off all other electronic appliances like televisions and radios.
4. Press the test button on your RCD without holding it down. At this point, the RCD should operate by turning off the connected appliance. If the RCD fails to operate, it’s advisable to have it inspected by a professional.
5. After pressing the test button and the RCDs have turned off, check if your small lamp is now switched off. Move the lamp across different power points and verify that it does not turn on when plugged into any of them.
6. Once your testing is complete, switch the RCD back on and ensure that the lamp functions properly when plugged into a power point.
Regularly testing your RCDs helps ensure their effectiveness and enhances the safety of your electrical system. Stay vigilant and conduct these tests at appropriate intervals.
siemens residual current device
Siemens is a reputable brand that offers residual current devices (RCDs) for electrical installations. RCDs, also known as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), play a crucial role in electrical safety by quickly disconnecting the power supply when they detect a leakage to earth.
Siemens RCDs are designed with advanced technology and built to meet safety standards. They provide protection against electric shocks and reduce the risk of electrical fires caused by faults. Siemens RCDs are available in various types and configurations to suit different applications and electrical systems.
When installing Siemens RCDs, it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and comply with local regulations for correct fitting and testing. Regularly testing Siemens RCDs ensures their reliability and effectiveness in protecting lives and property from electrical hazards.
If you have any specific questions about Siemens RCDs order and buy or need further assistance, feel free to ask
abb residual current devices
ABB is another well-known brand that offers residual current devices (RCDs) for electrical installations. RCDs, also known as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), are devices designed to protect against electrical shocks and prevent electrical fires caused by faults.
ABB RCDs are built with advanced technology to detect the imbalance in electrical currents between the live and neutral conductors. When an imbalance is detected, the RCD quickly disconnects the power supply, offering enhanced safety for individuals and properties.
ABB offers a wide range of RCDs with different current ratings, sensitivity levels, and features to suit various applications and electrical systems. Their RCDs are designed to meet stringent safety standards and are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
When installing ABB RCDs, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and adhere to local regulations to ensure proper installation and functionality. Regular testing and maintenance of ABB RCDs are essential to ensure they continue to provide reliable protection.
If you have any specific questions about ABB RCDs order and buy or need further assistance, feel free to ask
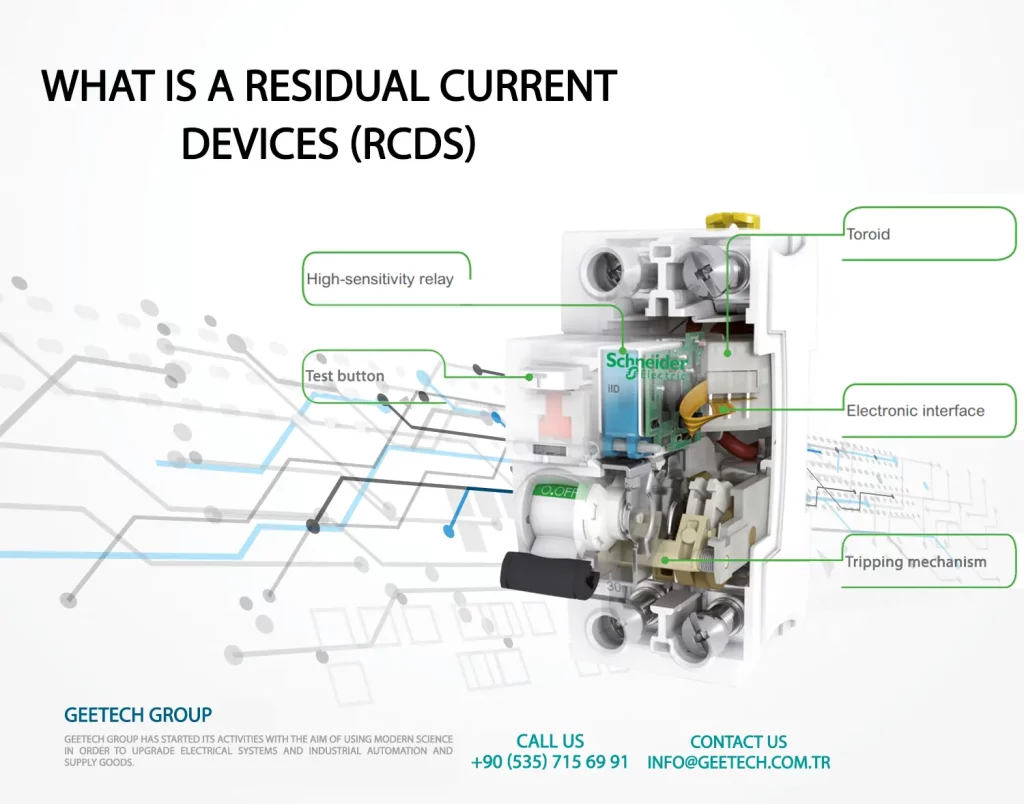
residual current device schneider
Schneider Electric is another reputable manufacturer known for producing residual current devices (RCDs) as part of their electrical product portfolio. RCDs, also referred to as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), play a critical role in electrical safety by detecting and protecting against electrical faults and ground faults.
Schneider Electric offers a range of RCDs with varying features, specifications, and applications. These devices are designed to monitor the flow of electric current and quickly interrupt the circuit when a fault is detected, reducing the risk of electric shock and fire hazards.
Schneider RCDs are built using advanced technology and adhere to strict safety standards. They are suitable for various installations, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
When installing Schneider RCDs, it is important to carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions and comply with relevant electrical codes and regulations. Regular testing and maintenance of RCDs are recommended to ensure their continued effectiveness.
If you have any specific questions about Schneider RCDs order and buy or need further assistance, feel free to ask
residual current device price
To get the price list and free consultation of residual current devices, you can contact our colleagues at GeeTech Group