When it comes to electrical safety, circuit breakers play a vital role. Among the commonly used circuit breakers are RCBO and RCCB, which offer protection for devices, circuits, and individuals by monitoring current flow.
Nonetheless, distinguishing between RCBO and RCCB can be challenging for many. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the differences between RCBO and RCCB, empowering you to choose the most suitable option for your specific requirements.
What is a Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB)?
A residual current circuit breaker (RCCB) is a crucial safety tool in electrical systems, designed to identify and interrupt electrical circuits in cases of leakage current. By swiftly interrupting the circuit, RCCBs prevent potential fires and safeguard individuals from dangerous electric shocks.
Working Principle of RCCB
The operation of an RCCB is rooted in Kirchhoff’s current law, which dictates that the total current entering a node must equal the total current exiting the node. Under normal circumstances, the currents through the live and neutral wires should be balanced and equal but opposite.
Nevertheless, in faulty conditions, an imbalance in the live and neutral currents, known as residual currents, occurs. For instance, when a person comes into contact with a live wire, a portion of the current may disperse to the ground through an alternate route. This divergence is precisely what an RCCB identifies and swiftly triggers the circuit interruption within milliseconds.
Main Function of RCCB
The primary role of an RCCB is to offer earth fault protection by constantly monitoring the disparity in current levels between the live and neutral wires. If the residual current stemming from a fault surpasses set thresholds, the RCCB swiftly interrupts the circuit, thereby safeguarding against electric shocks and potential hazards.
Types of RCCB
Residual Current Circuit Breakers (RCCBs) are available in various types distinguished by design features and specific functionalities. Classification is typically based on pole number (2 pole and 4 pole) and tripping curve characteristics (AC, A, B, and F). Here’s a brief overview of the diverse RCCB types:
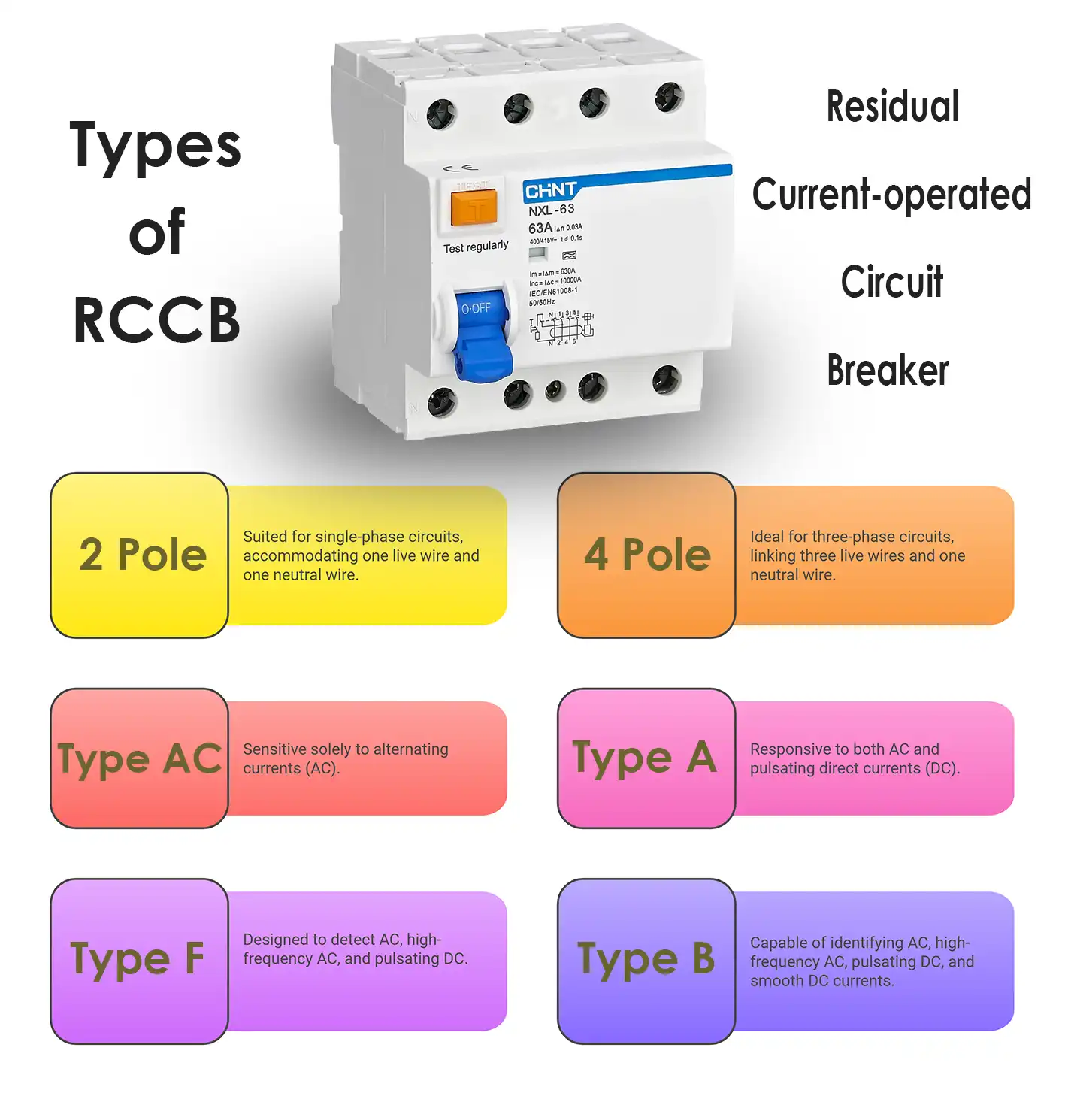
2 Pole: Suited for single-phase circuits, accommodating one live wire and one neutral wire.
4 Pole: Ideal for three-phase circuits, linking three live wires and one neutral wire.
Type AC: Sensitive solely to alternating currents (AC).
Type A: Responsive to both AC and pulsating direct currents (DC).
Type F: Designed to detect AC, high-frequency AC, and pulsating DC.
Type B: Capable of identifying AC, high-frequency AC, pulsating DC, and smooth DC currents.
These variations in RCCBs cater to a range of applications across residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
What is a Residual Current-operated Circuit Breaker (RCBO)?
In the realm of electrical protection devices, RCBO – or Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection – offers enhanced safety features compared to RCCBs. RCBOs safeguard against both residual current faults and overloads, boosting protection against short circuits as well.
Working Principle of RCBO
The operational mechanism of an RCBO in detecting earth leakage aligns with Kirchhoff’s principle, ensuring equilibrium between incoming and outgoing currents. By continuously monitoring disparities in current between live and neutral lines, an RCBO severs the circuit upon detecting a variance beyond preset safety limits.
Similar to standard MCBs, the functionality of an RCBO in responding to overcurrent is primarily governed by electromagnetic induction and the utilization of bimetallic strips. In instances of short circuits, the electromagnetic trip coil within the RCBO promptly triggers to deactivate the circuit.
Additionally, in cases of electrical overload from connected devices, the bimetallic strip flexes to initiate the circuit breaker’s trip mechanism.
Main Functions of RCBO
The operational principle of an RCBO underscores three key functions:
1. Shielding against earth fault currents
2. Safeguarding against overcurrent caused by overloading
3. Defense against short circuit currents
In essence, an RCBO serves as a comprehensive multifunctional device designed to safeguard both domestic and industrial electrical systems against a range of potential electrical faults and hazards.
RCBO and RCCB: Key Differences
Reviewing the fundamental disparities between RCBO and RCCB highlights the superior protective capabilities of RCBOs over RCCBs. While a RCBO defends against both earth faults and overcurrent, an RCCB solely guards against earth faults.
In addition, typically, an RCBO incurs a higher initial investment in comparison to an RCCB. This leads many individuals to opt for connecting an RCCB to an MCB to achieve a similar level of protection as offered by an RCBO.
Conclusion
RCBO and RCCB serve as popular circuit breakers widely utilized in various applications. From the detailed comparison provided above, it is apparent that an RCBO safeguards against both earth faults (residual current) and overcurrent, whereas an RCCB focuses solely on earth leakage protection.
Nonetheless, when choosing between circuit breakers, factors such as budget and compatibility with existing systems should also be taken into consideration.