How to Read the Nameplate of a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) for Accurate Installation
A miniature circuit breaker, commonly known as an MCB, is a vital component that provides effective protection to electrical circuits against short-circuits and overloads in various settings such as homes, commercial properties, and more.
These compact devices not only safeguard circuits but also serve as load switches. Widely employed in buildings, MCBs are seamlessly compatible with distribution boards. It is essential for both electricians and homeowners to understand how to accurately interpret the nameplate details of MCBs for safe and reliable installation and operation.
To explore a wide range of industrial MCB options, including the Schneider Acti 9 series, click here.
Why Understanding the MCB Nameplate is Important
The nameplate on a miniature circuit breaker is filled with vital technical details that determine its safety ratings and intended applications. Failing to correctly interpret these specifications can compromise the protection of electrical circuits and equipment. It is essential for installers to ensure that the chosen MCB aligns with the circuit requirements for voltage, current, and breaking capacity.
Homeowners should also grasp the information on the nameplate to effectively maintain the MCB units within their electrical panels. Misinterpreting the technical information could result in issues such as overloading, short-circuiting, and long-term safety risks.
Nameplate Information Breakdown
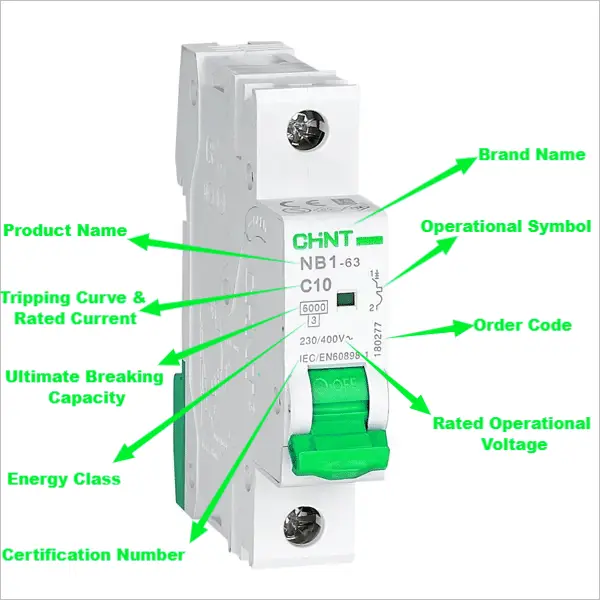

Exploring Vital Nameplate Details with the CHINT NB1-63 Miniature Circuit Breaker :
Brand Name
In the upper-left corner, the prominent brand name “BRAND” serves as a clear indicator of the manufacturer responsible for the design, testing, and warranty of the circuit breaker’s performance.
Product Name
In the heart of the nameplate lies the product identifier “NB1-63,” a crucial designation for the specific miniature circuit breaker model. This precise labeling aids electricians in accessing technical documents and identifying compatible spare parts with ease.
Order Code
Towards the top-right corner, the vertically arranged order code “180277” facilitates precise tracking and easy reordering when necessary.
Tripping Curve and Rated Current
Identified as “C10,” the tripping curve designated as “C” delineates the current-time characteristics for triggering under overloads or faults. The numeral “10” denotes the rated current value, indicating the maximum load current (10A) that this breaker safeguards.
Rated Operational Voltage
The operational voltage rating of “230/400V” encompasses both single and three-phase power system voltages to guarantee safe interruption during normal operations or fault conditions.
Ultimate Breaking Capacity
With a value of “6000”, this indicates that the breaker is capable of effectively clearing severe short-circuit faults without incurring damage or emitting hot gas.
Energy Class
The number “3” represents the energy absorption capacity during tripping designed to reduce arcing and spatter, ensuring user safety.
Certification Number
This certification, known as “IEC/EN 60898-1,” confirms that the miniature circuit breaker meets global product standards for construction and performance testing.
Operational Symbol
Positioned visually on the right side, the status symbol offers a quick visual cue outside the distribution board for verifying isolation.
key Features of Siemens and Schneider Miniature Circuit Breakers
GEETECH Group has started its activities with the aim of using modern science in order to upgrade electrical systems and industrial automation and supply goods. Click on the links below to view Schneider and Siemens products :
Key features of Siemens Miniature Circuit Breakers include:
- High quality and reliability
- Compact size for space efficiency
- Precision engineering for optimal performance
- Wide range of current ratings available
- Easy installation and maintenance
- Enhanced safety features for protection against electrical faults
Key features of Schneider Miniature Circuit Breakers include:
- Compact size for efficient space utilization
- High breaking capacity to effectively handle overloads and faults
- Reliable tripping mechanism for enhanced safety
- Easy installation and maintenance
- Wide range of current ratings available
- Designed for optimal performance and durability
Conclusion
Familiarity with nameplate markings is essential for selecting and installing MCBs that provide maximum safety and reliability. With nearly forty years of experience in smart energy solutions and a global presence backed by strong R&D, Siemens and Schneider stand out as trusted providers.
Whether you are a homeowner or a professional, rely on Siemens and Schneider MCBs to effectively manage your power distribution and prevent hazards from overloads or short circuits. To discover the full range of power distribution products offered by Siemens and Schneider, visit the GeeTech Group website.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to Read and Understand Circuit Breaker Labels?
A typical circuit breaker label includes the following key details:
✅1. Brand Name and Serial Number: Identifies the manufacturer and specific product.
✅2. Amperage Rating: Indicates the maximum current the breaker can handle before tripping, such as 5KA or 10KA.
✅3. Voltage Rating: Common ratings are 110V, 220V, or 240V, specifying the voltage the breaker is designed for.
✅4. Frequency (Hz) Rating: Refers to the line frequency (typically 50Hz or 60Hz) the breaker can manage.
How to Read the Numbers on a Circuit Breaker?
✅ The numbers on a circuit breaker indicate how much electrical current (measured in amps) can pass through the circuit before the breaker trips. For example, a breaker labeled "15" allows 15 amps to flow, but will cut off the circuit if it detects 16 amps or more. This is a critical safety feature designed to prevent electrical overloads.
Understanding the Numbers on MCBs: What Do kA Ratings Mean?
✅ The numbers on a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) represent its Short Circuit Rating, measured in kiloamperes (kA). In domestic installations, MCBs are typically rated at 6kA (6000 amps). This rating indicates the maximum short circuit current the MCB can safely interrupt. Given the standard household voltage of 240V, the over-current in a typical short-circuit scenario should not exceed 6000 amps to ensure protection against electrical hazards.
How to Read an MCCB? Key Features and Ratings Explained
✅ 1. Rated Current (In): This represents the tripping point of the MCCB during overload protection. It defines the maximum current that can flow without tripping.
✅ 2. Rated Frame Current (Inm): The maximum current the MCCB can handle under normal conditions.
✅ 3. Rated Working Voltage (Ue): The voltage rating for continuous operation of the MCCB, indicating the safe voltage range for its regular use.
How to Identify Different Types of Circuit Breakers?
✅ To determine what type of circuit breaker you have, follow these steps:
1. Check the Label: Look at the label on the circuit breaker box. If it's not visible on the exterior, open the panel door and look for the label inside.
2. Find Manufacturer Information: The label should include the manufacturer’s name, model number, and key specifications of the breaker.
If no label is present, you may need to consult an electrician for further identification.