Introduction
In today’s industrial and commercial landscape, energy efficiency and operational cost reduction are critical goals for every organization. One of the most effective yet often overlooked solutions to achieve both is the soft starter — an intelligent motor control device designed to reduce inrush current and mechanical stress during startup.
Soft starters not only help improve system reliability and equipment lifespan but also play a vital role in reducing maintenance costs and supporting sustainable operations. In this article, we’ll explore how soft starters work, their key components, and how they contribute to higher efficiency and lower energy consumption across industries.
What Is a Soft Starter?
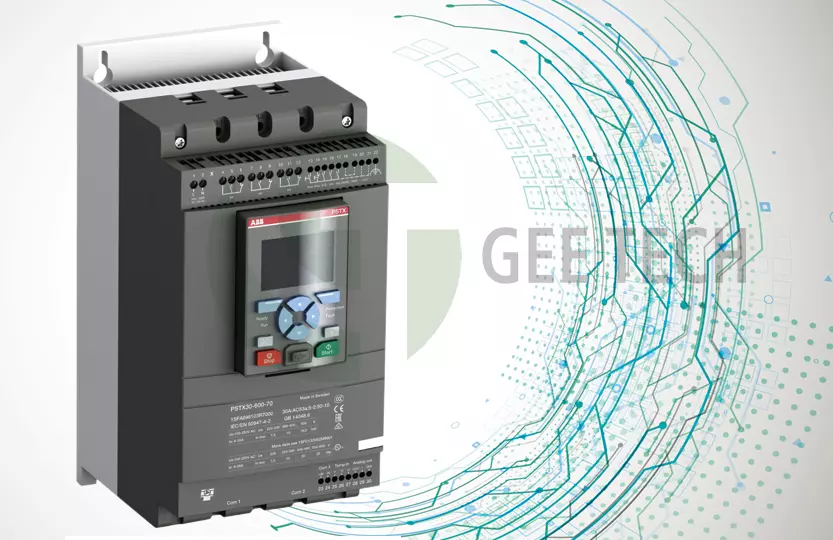
A soft starter is an electronic motor control device that gradually increases the voltage applied to an electric motor, allowing smooth acceleration and deceleration.
Unlike Direct-On-Line (DOL) starters, which apply full voltage instantly, soft starters gently ramp up power, minimizing starting torque, voltage dips, and mechanical stress on both the motor and connected equipment such as pumps, conveyors, and compressors.
This controlled startup significantly reduces mechanical wear and electrical strain, ensuring smoother operations and longer equipment life.
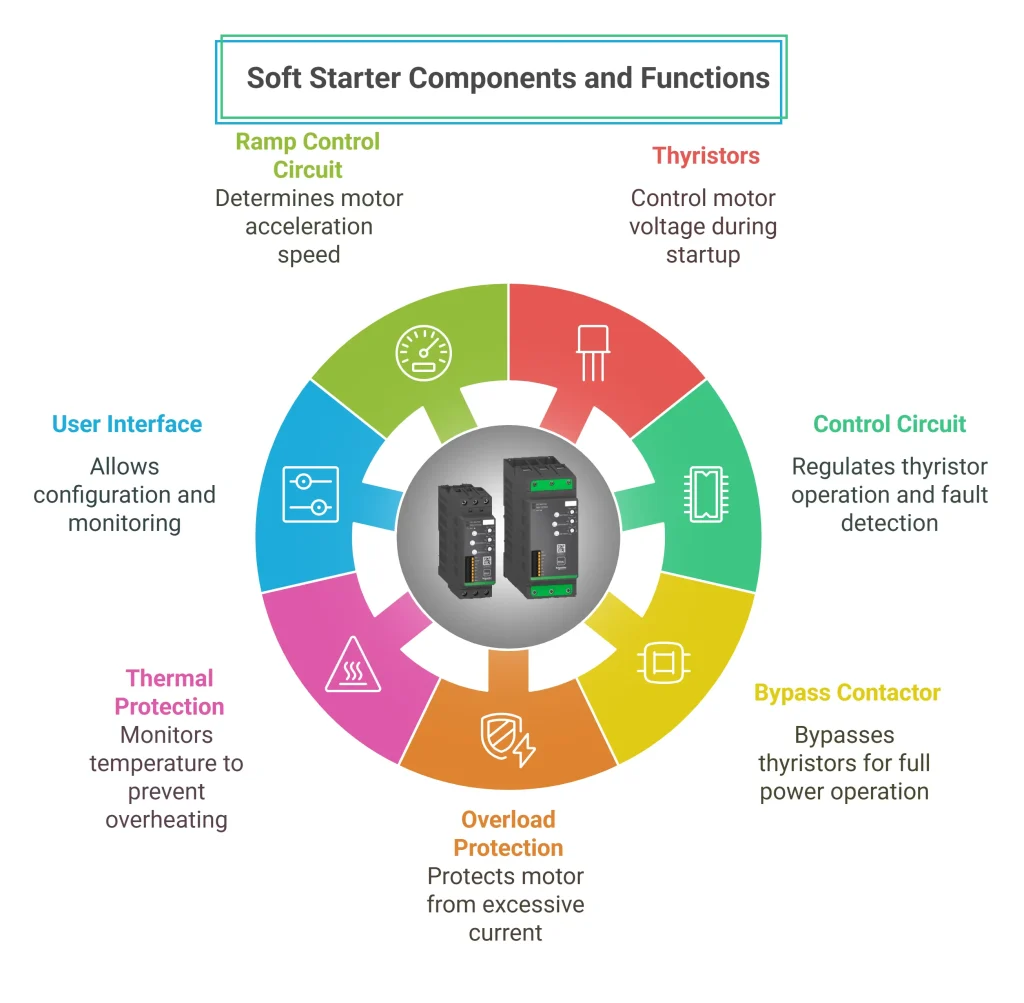
Key Components of a Soft Starter
1. Thyristors (Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers – SCRs)
Thyristors are semiconductor switches that regulate the voltage during motor startup. They gradually increase voltage levels, reducing inrush current and preventing power system disturbances.
2. Control Circuit
The control circuit manages the firing angles of the thyristors, ensuring a smooth voltage ramp-up. It also handles motor protection, fault detection, and operational sequencing.
3. Bypass Contactor
Once the motor reaches full speed, the bypass contactor engages, bypassing the thyristors. This increases efficiency and reduces heat dissipation within the soft starter.
4. Overload Protection
Built-in overload protection monitors current flow. If excessive current is detected, the soft starter limits it, preventing overheating and potential motor damage.
5. Thermal Protection
The soft starter continuously monitors temperature. If thresholds are exceeded, it triggers alarms or automatically shuts down the motor to prevent damage.
6. Human-Machine Interface (HMI)
Modern soft starters feature a digital HMI that allows operators to configure parameters, adjust ramp time, set voltage limits, and view real-time status for easy operation and maintenance.
7. Ramp Control Circuit
This circuit determines how quickly voltage increases during startup, ensuring gradual acceleration, reducing stress, and protecting connected machinery.
Key Features and Benefits of Soft Starters
Controlled motor startup and stop
Lower inrush current and reduced power surges
Less mechanical wear on motors and equipment
Extended equipment lifespan
Compact design with easy integration
Enhanced protection and diagnostics
Improved power quality and reduced voltage dips
Working Principle of a Soft Starter
The core principle of a soft starter is controlled voltage ramp-up during motor startup.
Instead of applying full voltage instantly, the soft starter uses thyristors (SCRs) to deliver a progressive increase in voltage, controlling current flow and torque output.
During Start: Voltage gradually increases, limiting current spikes and mechanical stress.
During Operation: The bypass contactor takes over, improving efficiency.
During Stop: Voltage ramps down smoothly, avoiding abrupt halts — ideal for systems like pumps and conveyors.
This precise control over starting and stopping reduces electrical surges, equipment wear, and system downtime.
Controlled Voltage Ramp-Up
Instead of applying full voltage instantly—as in direct-on-line (DOL) starts—a soft starter progressively feeds current to the motor. This controlled voltage ramp-up reduces initial inrush current and limits starting torque, making it especially suitable for three-phase induction motors.
Role of Thyristors and SCRs
Soft starters primarily rely on thyristors, or silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs), which act as high-speed semiconductor switches. These components adjust the voltage supplied to the motor without altering its frequency, enabling precise control over motor startup behavior.
Each SCR has four layers of semiconductor material and operates in response to gate signals from the control circuitry. By adjusting the firing angle of the SCRs, the soft starter smoothly regulates the power flow during acceleration.
Protection Against Electrical and Mechanical Stress
By limiting the voltage and torque at startup, soft starters prevent sudden mechanical shocks and electrical spikes that could otherwise damage the motor windings or connected systems. This reduces the risk of overheating, energy waste, and costly maintenance.
Start/Stop Functionality
Soft starters also include control settings for both startup and shutdown. During shutdown, the soft starter can ramp down the voltage instead of cutting power instantly, minimizing electrical wear and enabling soft stops where required—ideal for pumps, fans, and conveyors.
Voltage Limitation and Parameter Settings
Advanced models allow users to configure voltage thresholds and ramp times through a user interface or digital panel. These parameters ensure that the motor does not exceed a safe voltage level during operation, adding an extra layer of protection against overcurrent or voltage surges.
How Soft Starters Improve Energy Efficiency
A major advantage of using soft starters is energy efficiency improvement, particularly during motor startup. When motors start at full voltage, the inrush current can be 6 to 8 times higher than the rated current. This surge not only strains the motor but also spikes energy consumption.
By limiting the inrush current:
- Soft starters lower peak demand charges on electrical systems
- Reduce voltage dips in the network
- Help maintain power quality
- Support compliance with energy-saving initiatives
Though soft starters don’t reduce energy during steady-state motor operation (unlike variable frequency drives), they significantly cut energy waste during frequent starts and stops — making them ideal for applications like HVAC systems, conveyors, and water pumps.
Lower Maintenance Costs and Equipment Longevity
Frequent startups at high torque can degrade mechanical components such as bearings, shafts, belts, and couplings. Soft starters minimize mechanical shock, which leads to:
- Less wear and tear on motors and attached machinery
- Extended lifespan of motors and production equipment
- Reduced frequency of repairs
- Lower total cost of ownership (TCO)
Additionally, soft starters prevent thermal and electrical stress on motor windings, reducing the risk of insulation damage or early motor failure. Over time, this translates into fewer unplanned downtimes and optimized maintenance schedules.
Additional Benefits of Soft Starters
Compact design: Easy to integrate into existing control panels
Lower installation costs: Fewer components compared to alternative control methods
Enhanced safety: Reduced risk of electrical and mechanical failures
Improved system uptime: Smooth starts and stops prevent sudden breakdowns
Applications Across Industries
Soft starters are used in a wide range of sectors, including:
Industrial Plants: Conveyor systems, compressors, mixers, and crushers
Water & Wastewater Treatment: Pumps and aeration systems
Agriculture: Irrigation and ventilation motors
HVAC Systems: Fans, chillers, and compressors
Mining & Oil and Gas: Heavy-duty motor applications
Material Handling: Elevators, cranes, and transport systems
Their versatility and reliability make soft starters a cornerstone of modern motor control.
Conclusion
Investing in a soft starter is a smart, cost-effective strategy for industries focused on energy efficiency, system reliability, and equipment longevity.
By controlling startup current and reducing mechanical stress, soft starters:
Enhance energy performance
Extend equipment life
Lower maintenance costs
Support sustainable, efficient operations
From manufacturing to water management, soft starters help businesses cut costs, increase productivity, and build greener, more reliable systems.
Contact Us