In this article from the GeeTech Group knowledge series, we explore the Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) — its definition, structure, uses, and the most trusted UPS brands in the market.
Table of contents of this article
- What is a ups
- What is a UPS battery system
- What is a UPS system
- What is a UPS computer
- types of UPS
- How do UPS Systems work
- Best UPS Brand
What is a UPS
A UPS typically consists of:
Batteries that store electrical energy.
An inverter that converts stored DC power into usable AC power.
They come in various sizes and capacities, ranging from small home units to large-scale enterprise and data center solutions.
What is a UPS Battery System
A UPS battery system is the heart of any UPS setup. It stores the electrical energy required to keep devices running during a power outage.
When mains power fails, the UPS battery system activates, supplying energy to the connected devices until power is restored or a safe shutdown can occur. The type, capacity, and quality of these batteries significantly impact the UPS performance and reliability.

What is a UPS System
A UPS system ensures continuous power for critical devices during power failures or fluctuations. It is commonly used to protect:
Servers and data centers
Networking and telecom equipment
Healthcare and financial systems
Industrial automation and manufacturing lines
By switching to battery power instantly, UPS systems prevent data loss, operational downtime, and equipment damage.
What is a UPS Computer
A UPS for computers is specifically designed to protect desktops, workstations, and IT equipment from:
Power surges
Spikes and brownouts
Complete power outages
Key components of a UPS for computers include:
Battery Backup – Keeps the computer running temporarily during outages.
Surge Protection – Prevents damage from sudden voltage spikes.
Automatic Voltage Regulation (AVR) – Maintains stable voltage.
Monitoring Software – Manages power events and automated safe shutdowns.
Types Of UPS
There are three main UPS technologies:
Standby UPS – Switches to battery power during outages; cost-effective for basic protection.
Line-Interactive UPS – Corrects minor voltage fluctuations without using the battery, offering better protection.
Online UPS – Provides continuous power through the inverter, ensuring the highest level of protection against all power anomalies.
How Do UPS Systems Work
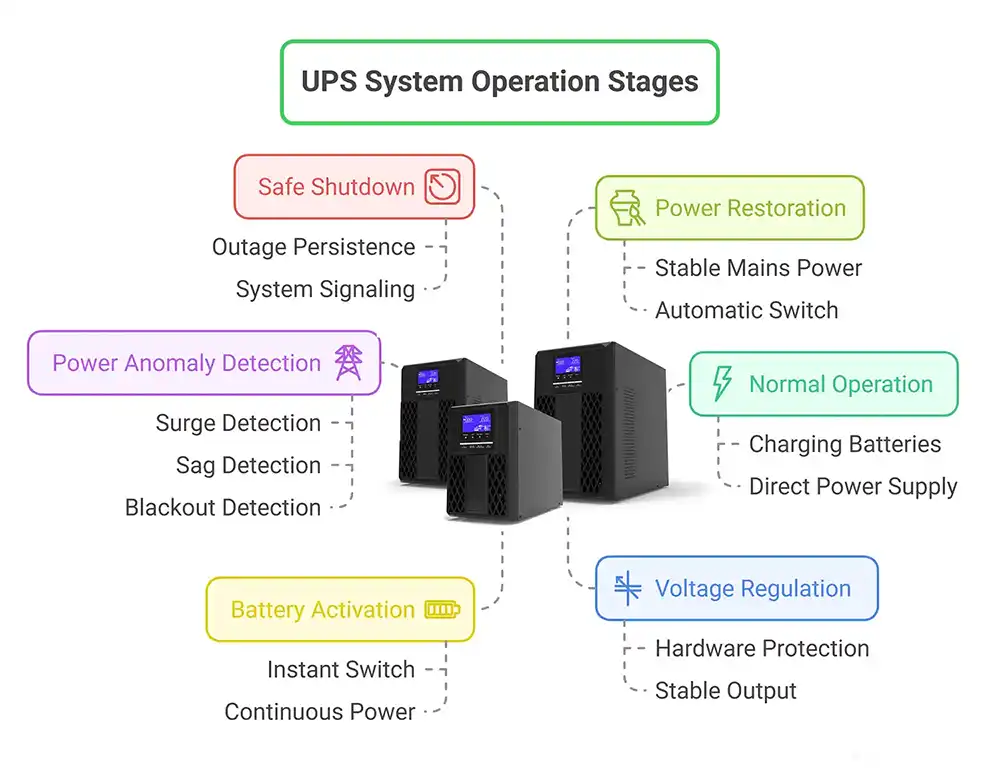
UPS units operate in several stages:
Normal Operation – Passes electricity directly to devices while charging batteries.
Power Anomaly Detection – Monitors voltage; instantly detects surges, sags, or blackouts.
Battery Activation – Switches to stored battery power to keep devices running.
Voltage Regulation – Stabilizes output to prevent hardware stress.
Safe Shutdown – Signals connected systems to power down gracefully if the outage persists.
Power Restoration – Returns to mains power once stable.
Best UPS Brand
When selecting a reliable UPS system, consider these trusted brands:
APC by Schneider Electric – Industry leader, robust for both home and enterprise.
CyberPower – Innovative and cost-effective solutions.
Tripp Lite – Proven reliability for diverse applications.
Eaton – High-end solutions for industrial and data center use.
Vertiv (formerly Emerson Network Power) – Mission-critical UPS solutions with advanced features.
When choosing, evaluate capacity, runtime, energy efficiency, scalability, warranty, and software management capabilities to match your specific needs.

Conclusion
In conclusion, an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is an essential safeguard for any environment where power stability matters — from personal computers to large-scale data centers. By providing immediate backup power, surge protection, and voltage regulation, UPS systems prevent costly downtime, protect sensitive electronics, and ensure operational continuity.
Whether you need a home UPS, a business-grade UPS, or a high-capacity industrial solution, selecting the right UPS type and brand is crucial. Investing in a quality UPS today means safeguarding your data, equipment, and productivity against unpredictable power disruptions tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a UPS?
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is a backup power device that keeps your equipment running during power outages, voltage fluctuations, or surges. Unlike a simple battery, a UPS also provides power conditioning—filtering out spikes, brownouts, and harmonic distortions to deliver clean and stable electricity. This makes a UPS essential for protecting sensitive devices such as computers, servers, and networking equipment.
What is a UPS computer?
A UPS for a computer is designed to supply emergency backup power when electricity fails. It allows your computer to keep running long enough to save your work, safely shut down, or continue operating through short outages. By acting as both a battery backup and a surge protector, a UPS prevents sudden data loss and hardware damage caused by unexpected power cuts.
What is a UPS used for?
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) is used to:
✅Protect computers, servers, and IT equipment from sudden shutdowns.
✅Provide backup power during blackouts.
✅Stabilize voltage and filter electrical noise.
✅Prevent data loss, equipment damage, and downtime.
Whether for home computers, data centers, or industrial machines, a UPS ensures continuous and safe operation.
What is UPS in inverter?
While often confused, an inverter and a UPS are not the same.
✅UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply): Provides instant power backup with almost zero switching time, making it ideal for computers and sensitive electronics.
✅Inverter: Converts DC (from batteries) to AC to power appliances, usually with a slight delay when switching.
In short, a UPS is a specialized inverter system designed for uninterrupted, immediate power support.
What is a Smart UPS?
A Smart UPS is an advanced uninterruptible power supply that offers real-time monitoring, remote management, and intelligent power control. Unlike basic UPS units, Smart UPS systems integrate with your network, display battery health, and deliver higher reliability for critical applications. They are widely used in servers, data centers, and enterprise environments where uptime is crucial.
Contact GeeTech Group :